Punjab
The long wait: Since 2012, The Punjab Municipal Infrastructure Development Company (PMIDC) had tried to introduce an e-governance system across 167 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs). Despite floating multiple RFPs, it was unable to move forward in this direction primarily because of financial constraints and technical problems. The estimated cost of the program was prohibitive at ₹200-300Cr.
The bold decision: In March 2018, after a careful evaluation of all options, PMIDC decided to go with eGov’s open platform – DIGIT. The PMIDC team felt that this platform-based approach will be faster to roll out & enable the state to build its capacity at a much lower cost. As DIGIT already had majority of components & applications needed, this approach freed up resources to focus on critical non-technology elements like program management, governance, capacity building etc.
A partnership to drive citizen impact: PMIDC entered into a strategic partnership with eGov, by signing a non-commercial MoU. The intent was for eGov to support the state by:
Providing advisory support to PMIDC in program design and building its own IT and Operations team

Enabling and training Punjab Government personnel to customize, configure and support the platform independently

Resolving key technical and implementation issues with the state team
Impact Highlights
A new national benchmark – 100 ULBs in 90 days

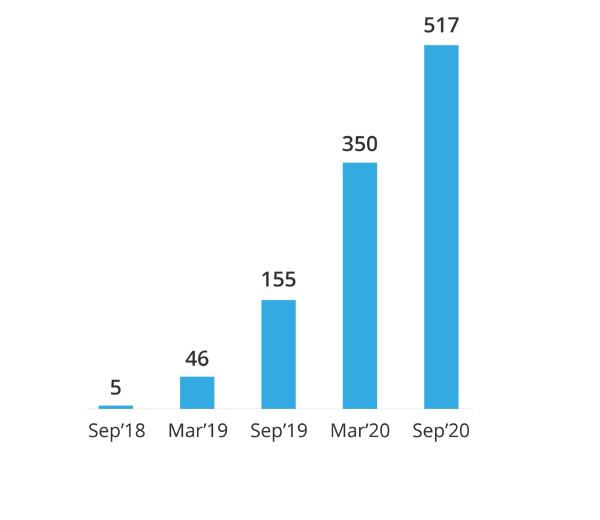
> ₹500 Cr
revenue collected
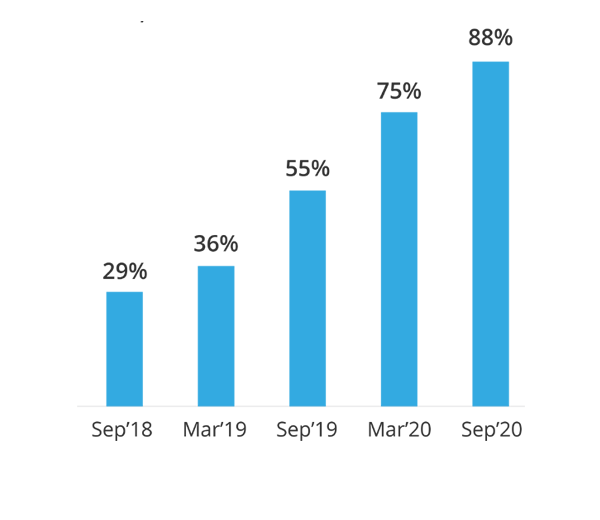
3 times improvement in resolving
complaints within SLA
By the
Numbers
- 167
ULBs live - 63
services
digitised - 4000+
employees
trained - ₹ 5-7 cr
total cost to state
- 517 cr
revenue collected - 77,000
complaints resolved - 14 lakh
citizen transactions
(As of Oct 2020)
An 'atmanirbhar' state team: Helping the state build capacity
From day one, the intent of both eGov and PMIDC was to build the state’s capacity to handle both technology and operations independently. This was a key priority for the strategic partnership, embodied in the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the partners.
In 2018, PMIDC created a 20-member program implementation team, with resources pulled in from various branches of the Punjab government. Since then, eGov has organized approximately 1,100 hours of enablement sessions in Bangalore, and more than 7,200 hrs of online training sessions to enable PMIDC resources in support and bug fixing, product customization, new product development, and maintenance of the hosting infrastructure. Altogether, 3,978 state and ULB employees have been trained on various aspects of the DIGIT platform.
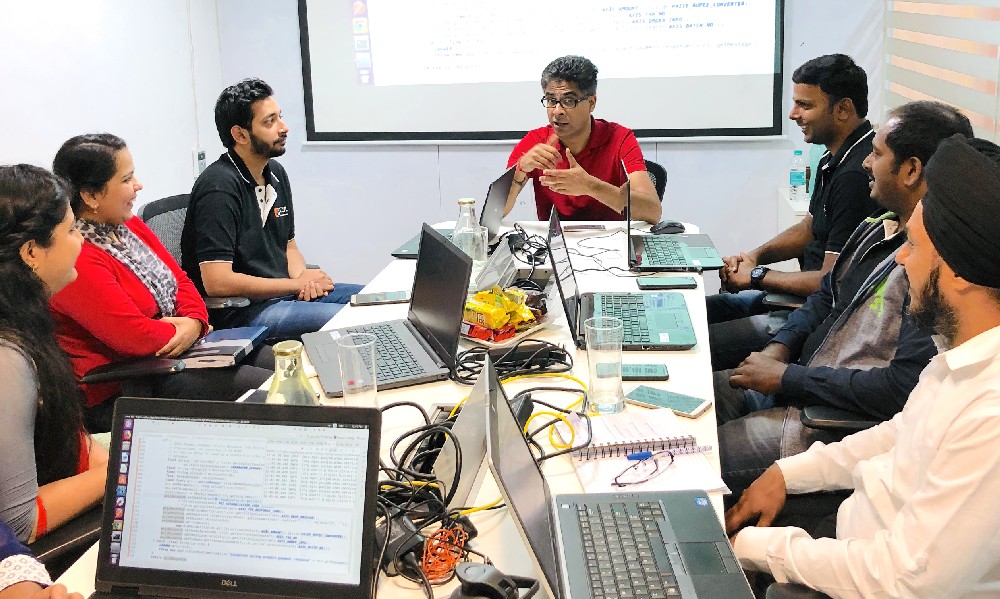

Enablement of PMIDC team on DIGIT

The best thing about our collaboration with eGov is that they are building our state team’s capacity and expertise so that we can get to a position where PMIDC can independently manage the platform and build new solutions on top of it. We are very happy that we went for this strategic partnership with eGov - finally the citizens of Punjab are getting all the municipal services digitally, and the ULB revenues are also improving.”
Shri Ajoy Sharma, IAS
(CEO, PMIDC)
Leveraging the platform, enabling innovation
To make it really easy to access municipal services, eGov and PMIDC have partnered to launch mSeva WhatsApp Chatbot. Now citizens can access services by simply chatting on WhatsApp. No need to download any app, or go to ULB offices.
Till date, two WhatsApp Chatbots have been launched in Punjab. The mSeva WhatsApp Chatbot has made filing and tracking grievances as easy as chatting with one’s friends, and removes the need for citizens to download even the mSeva mobile app. eGov and PMIDC are working to expand the range of services accessible through the mSeva Chatbot, and citizens in Punjab should soon be able to view and pay bills via WhatsApp as well.
The Home Isolation Chatbot enables citizens who are self-isolating during COVID in Punjab to directly update their daily health status over WhatsApp. This illustrates the flexibility and adaptability of the platform approach, as it was possible to rapidly develop a solution as part of the pandemic response by leveraging building blocks already available on the platform



